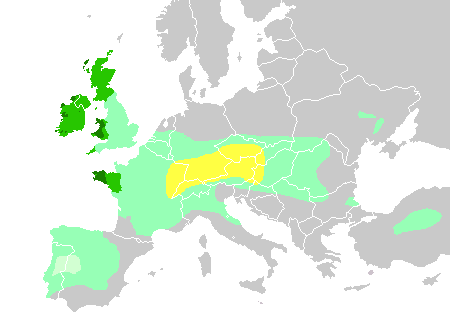
Prehistoria e historia de los pueblos celtas
El término celta (keltoi) es de origen griego, quienes pudieron haberlo tomado prestado de iberos o ligures. Los celtas probablemente se llamaban a sí mismos *gal-,[cita requerida]o sea: galos (derivados: gálata).
No se ha logrado discernir etnias propiamente celtas entre los primeros grupos de indoeuropeos que penetraron en la Europa central. Según el punto de vista tradicional, solo hasta el siglo V a. C. con el surgimiento de la cultura de La Tène es razonablemente seguro identificar a los portadores de esa cultura como hablantes de lenguas celtas. Desde un punto de vista igualmente tradicional, los primeros pobladores indoeuropeos podrían haber sido los portadores de la Cultura de los campos de urnas que se propagaron rápida y extensamente por Europa hacia el siglo XIII a. C. Los portadores de esta cultura se expandieron descendiendo por la margen derecha del Ródano ocupandoLanguedoc,Cataluña y el bajo valle del Ebro. Otra línea de expansión les llevó a Bélgica y el sureste británico.
Sin embargo, recientemente se ha asociado a los celtas o sus precursores inmediatos con la cultura del vaso campaniforme,3 que en el Neolíticomedio se habría expandido desde la península ibérica, difundiéndose por el frente Atlántico hasta el centro de Europa (zona media del Elba).4 Al confluir así con la cultura de la cerámica cordada se habría constituido el primer horizonte cultural Paneuropeo, que algo más tarde desembocaría en la cultura del bronce en Unetice, cerca de Praga. El estudio aún más reciente de la distibución del haplotipo mitocondrial H, no solo es consistente con estas hipótesis, sino concluye que esta difusión, que parte del SO de Europa, habría supuesto un importante movimiento de población, y no solo la transmisión de un “paquete cultural”.5


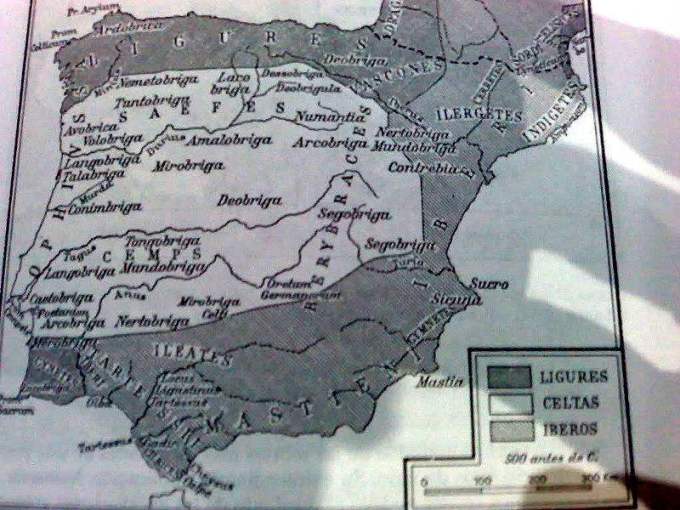
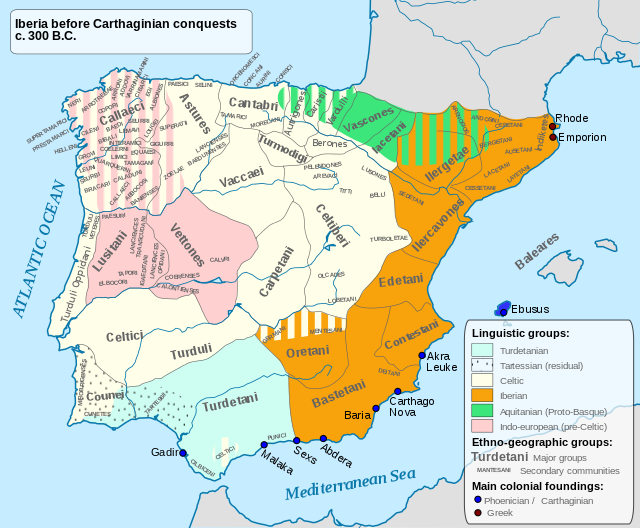
A partir del siglo VIII a. C., otos pueblos presuntamente indoeuropeos fueron los portadores de la cultura de Hallstatt (Hierro-I), extendiéndose en esta fase por el interior de lapenínsula ibérica (siglo VII a. C.) En elsiglo VI a. C. los pueblos presuntamente indoeuropeos fueron desplazados del noreste ibérico a manos de los iberos, quedando así los celtas de Iberiaaislados del resto de pueblos celtas continentales.

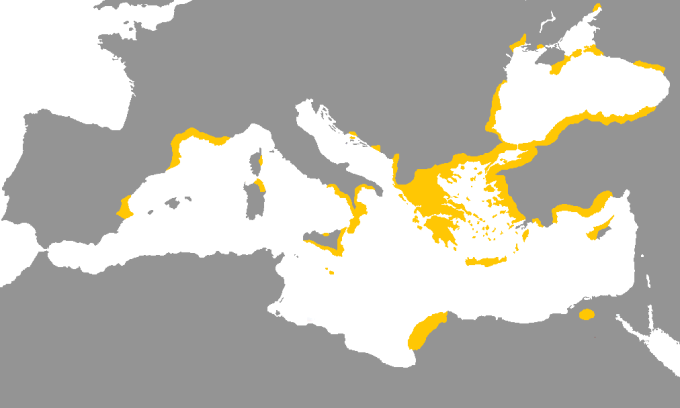
Desde el siglo IV a. C., los celtas continentales inauguran la cultura de La Tène, específicamente celta (Hierro II). En esta fase, los celtas acabaron de ocupar el norte y centro deFrancia (la Galia), el norte de Italia, así como la mayor parte de las islas británicas. También se extendieron por losBalcanes, alcanzando incluso una comarca de Asia Menor, que será conocida como Galatia. En esta época se construyen importantes villasfortificadas (lat. oppida), que sirven de centros comerciales y políticos. Es también en este período cuando el druidismo se extiende entre los celtas. Contrariamente a lo que se cree, los druidas no tenían templos de piedra ni arqueológicamente se ha podido enlazar el druidismo celta conStonehenge, siendo la cultura megalítica anterior en varios milenios a la cultura celta y al fenómero del druidismo. Este error de asociar la cultura megalítica atlántica (presente en las islas británicas, Francia y España) con Stonehenge está muy extendido entre la gente por ser un invento del romanticismo del siglo XVIII. Como ejemplo: los celtas ibéricos no conocieron el fenómeno druídico, pero en España hay muchos restos megalíticos.

Una de las primeras menciones de los celtas, es la de los galos senones cisalpinos liderados por su rey Breno, que llegaron a invadir Roma en el390 a. C. Posteriormente la república romana primero y el imperio romano después combatirían exitosamente a los galos cisalpinos y transalpinos.Julio César ya había luchado contra ellos durante su conquista de la Galia y, con el tiempo, los romanos les arrebataron también sus dominios británicos e ibéricos. A finales del Imperio romano (476 d. C), los celtas tan sólo ocupaban partes del noroeste de Francia, Irlanda, Gales y algunas zonas de Escocia. Durante el transcurso de la Edad Media, reforzaron su control de Escocia e hicieron varios intentos de ampliar su territorio enInglaterra. A partir del siglo II a. C., los celtas acusan la creciente presión militar de los germanos por el norte y, algo después, la de losromanos por el sur. En pocas décadas toda la Galia está ocupada por los romanos. La presencia romana en Gran Bretaña fue de escasa duración, lo que permitió a las lenguas celtas de esta isla (galés) sobrevivir y, más tarde, regresar al continente (Bretaña francesa).

Todavía en el siglo VII d. C. los celtas llevaron a cabo su quizá última expansión: los escotos irlandeses invadieron Caledonia, región que pasó a ser llamada Escocia.
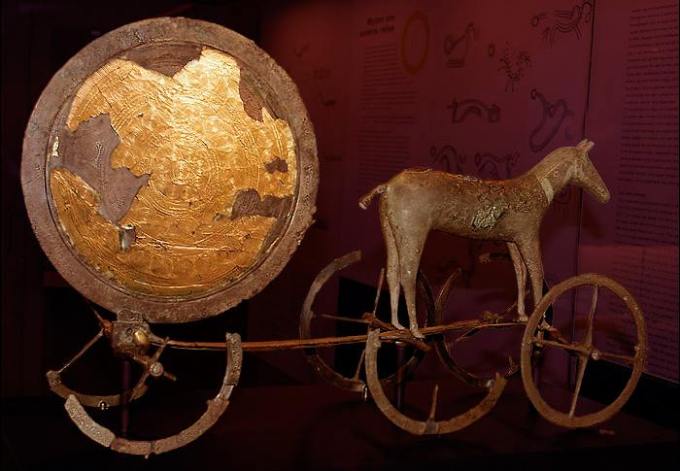
Entre los restos arqueológicos celtas destacan los castros y los petroglifos(nota: muchos petroglifos son mil años anteriores a la cultura celta, aunque se seguirán haciendo durante el periodo celta), que se encuentran con frecuencia en el noroeste de la península ibérica.
Los pueblos y cultura célticas tuvieron una fuerte presencia en el sudoeste de la península, documentada por Plinio el Viejo y otras fuentes. Según historiadores como Adolf Schulten el norte de la Península estaba habitado no por pueblos celtas sino por ligures.
_______________________………………………………..=========================
Prehistory and history of the Celts

The Celtic term (keltoi) is originally Greek , who could have borrowed fromIberians and Ligurians . The Celts probably called themselves * gal- , [citation needed ] ie: Gauls (derivatives gálata).
Not able to discern ethnic Celts themselves among the first groups of Indo-Europeans who entered Central Europe. According to the traditional view, only to the V century. C. with the emergence of the La Tène culture is reasonably safe to identify carriers of that culture as speakers of Celtic languages. From a traditional point of view also, the first Indo-European people could have been the carriers of the culture of the fields of urns that spread rapidly and extensively through Europe to the XIII century. C. The bearers of this culture expanded descending the right bank of the Rhoneoccupying Languedoc , Catalonia and the lower valley of the Ebro . Another line of expansion led them to Belgium and southeast Britain.

However, recently it has been associated with the Celts or their immediate precursors to the culture of Beaker , three in the Neolithicmeans would have expanded from the Iberian peninsula , spreading across the Atlantic off to central Europe (middle area of Elba ). 4 Al and merge with the Corded Ware culture would have been the first Pan-European cultural horizon , which would lead to something later bronze culture Unetice , near Prague. The more recent of the distibution of mitochondrial haplotype H study is not only consistent with these hypotheses, but finds that this broadcast, that part of the SW of Europe, would have been a considerable movement of population, not just the transmission of a ” cultural package “. 5


From the eighth century. C. , otos allegedly Indo-Europeans were the bearers of the Hallstatt culture (Iron-I), at this stage extending through the interior of the Iberian Peninsula(seventh century. C.) In the sixth century. C. The alleged Indo-European peoples were displaced northeastern Iberian hands of the Iberians and the Celts being Iberiaisolated from the rest of continental Celts.
From the fourth century. C. , the Continental Celtic culture inaugurated La Tène , specifically Celtic (Iron II). At this stage, the Celts ended up occupying the northern and centralFrance (the Gaul ), northern Italy, as well as most of the British Isles. Also spread the Balkans , reaching even a region of Asia Minor , to be known as Galatia . At this time important are constructed villas fortified (lat. oppida ) serving commercial and political centers. It is also during this period when Druidism extends between the Celts. Contrary to popular belief, the Druids were not archaeologically stone temples and has been linked with Celtic Druidism Stonehenge , megalithic culture being the previous several millennia in Celtic culture and fenómero Druidry. This mistake of associating the Atlantic Megalithic culture (present in the British Isles, France and Spain) with Stonehenge is widespread among people for being an invention of the eighteenth century romanticism. As an example: the Iberian Celts knew the Druidic phenomenon, but in Spain there are many megalithic remains.
One of the first mentions of the Celts is that of Cisalpine Gauls senones led by their king Breno , who came to invade Rome in 390. C. Subsequently, the first Roman Republic and the Roman Empire would fight successfully after the Cisalpine Gauls and Transalpine. Julius Caesar had battled them during his conquest of Gaul and, eventually, the Romans also seized their British Dominions and Iberian . At the end of the Roman Empire (476 d. C), the Celts occupied only parts of northwestern France, Ireland, Wales and parts of Scotland. During the course of the Middle Ages, reinforced its control of Scotland and made several attempts to expand its territory inEngland . From the second century. C. , the Celts accuse the increasing military pressure from the Germans to the north and, somewhat later, theRomans from the south. In a few decades the whole of Gaul is occupied by the Romans. The Roman presence in Britain was of short duration, which allowed the Celtic languages of this island ( Welsh ) survive and later return to the mainland ( Brittany ).
Still in the seventh century. C. Celts held their last expansion perhaps: theScots Irish invaded Caledonia , a region that became called Scotland .
Among the Celtic archaeological remains include the forts andpetroglyphs (note: many thousand petroglyphs are pre-Celtic culture years, but continue to do during the Celtic period), which is often found in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula.
The Celtic peoples and culture had a strong presence in the southwest of the peninsula, documented by Pliny the Elder and other sources. According to historians as Adolf Schulten the north of the peninsula was inhabited not by people but by Celtic Ligurians.
Fuente:
http://es.wikipedia.org